Introduction to Programming - Types of Languages, Memory Management
Let us discuss related to Types of Programming, Types of Memory Allocation ,Stack and Heap , Garbage Collection in this blog.

Lets explore Introduction to Programming and Memory Management .
Introduction
We need to give instructions to the computer in order to perform the task.
In order to perform a task we need to give instructions to the computer to perform tasks.
Computers understand only 0's and 1's .
- A language used by programmers to communicate with the computer is called as a programming language.
There are different types of Programming Languages.
Namely :
Procedural Language .
Functional Language.
Object oriented Language .
As we got to know regarding types lets go to the actual meanings regarding the types of programming languages.
1. Procedural Language:
Procedural Language specifies steps of well structured steps and procedures to compose a program.
This type contains systematic order of Statements ,Functions and Commands to complete the task.
We can consider C,C++,Java as Procedural Programming.
We can also consider loops, switch and case statements in this type.
Ex: int a = 10;
2. Functional Language:
Functional Language can be stated as writing a program in Pure Functions.
Pure functions: Pure functions are those which we can never modify variables
but create new ones as an output.
The Functional Language is used in situations where we can perform lots of
different operations on the same set of data like ML.
Ex:
a = 10 a = "Lavanya"
In this case if the object is not used it is sent to Garbage Collection.
Garbage Collection: *Objects which don't have a reference variable pointing towards
the object will be moved to garbage collection. *
- We can consider python as Functional Language and Procedural Language.
First class functions: In short ->Reassigning variables.
3. Object-Oriented Programming Language:
Object Oriented Programming language revolves around Objects.
Code + Data =Object.
- Related to object, class and some subsequent words we will see in further series.
- Object oriented programming is developed to make it easier to develop, debug, reuse
and maintain software.
Used to develop code in chunks (small version)to make it easier.
As we explored Programming and its types now lets discuss related to Memory Allocation
in brief.
There are two types of Memory Allocation namely
Static Allocation.
Dynamic Allocation.
1. Static Allocation:
Performs checking at compile time.
Errors show at compile time.
We need to declare datatype before using the code.
In this type we can have more control on code.
Ex:
int a = 10;
In Java , if we don't specify the datatype it shows error in the compile time itself.
i.e., At the time of compilation.
2. Dynamic Allocation:
Performs checking at Run time.
Errors cannot be identified easily.
No need to declare datatype.
Saves time in writing the code but might show errors at run time.
Ex:
a = 10
In Python the errors are shown after compilation.(Run Time).
Compile Time: Compile time refers to the time duration in which the programming code is converted to the machine code (i.e., binary code) and usually occurs before runtime.
Run Time: Runtime is the period of time when a program is running. It begins when a program is opened (or executed) and ends with the program is quit or closed. Runtime is a technical term, used most often in software development.
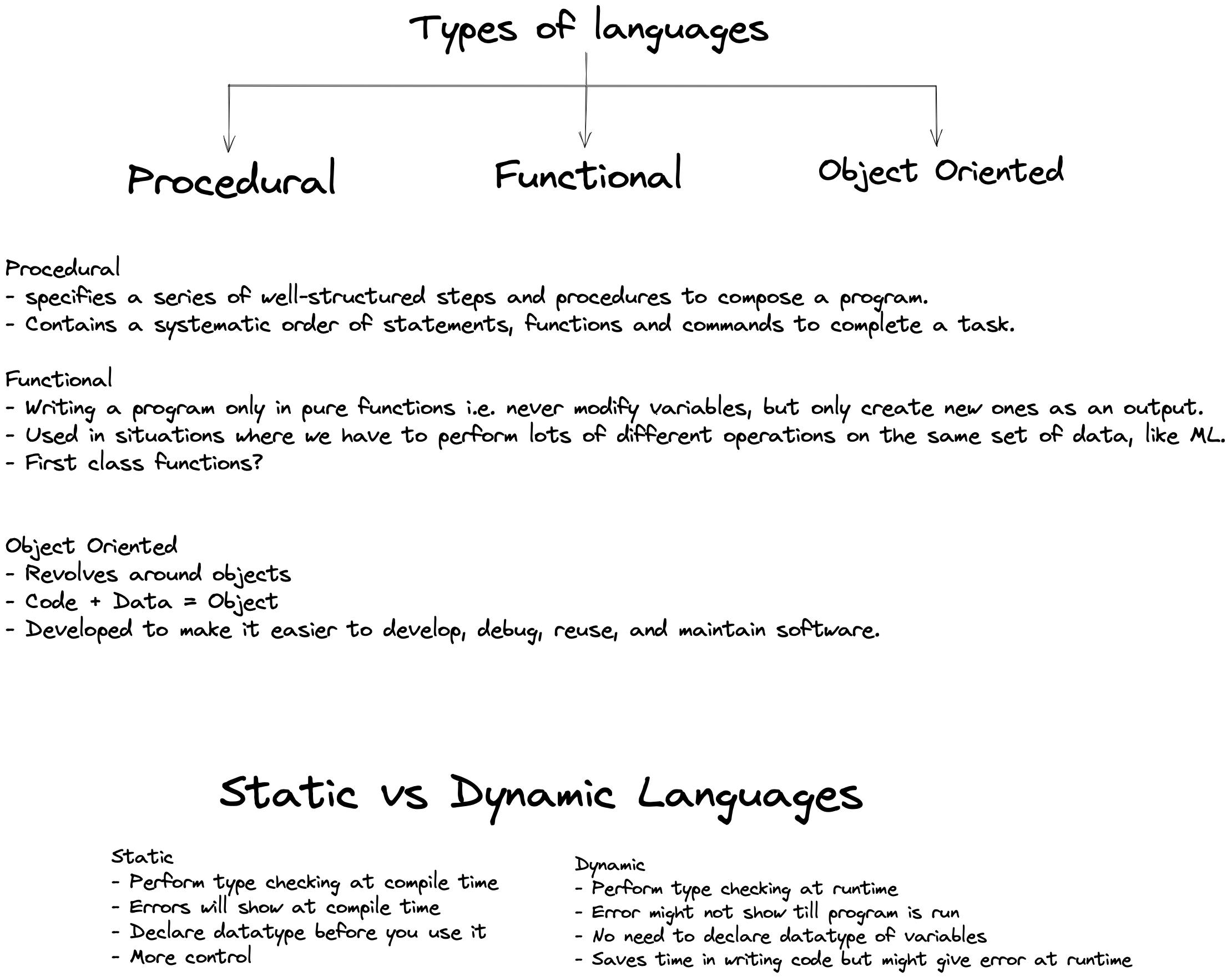
Image Credits: KunalKushwaha
Stack and Heap.#
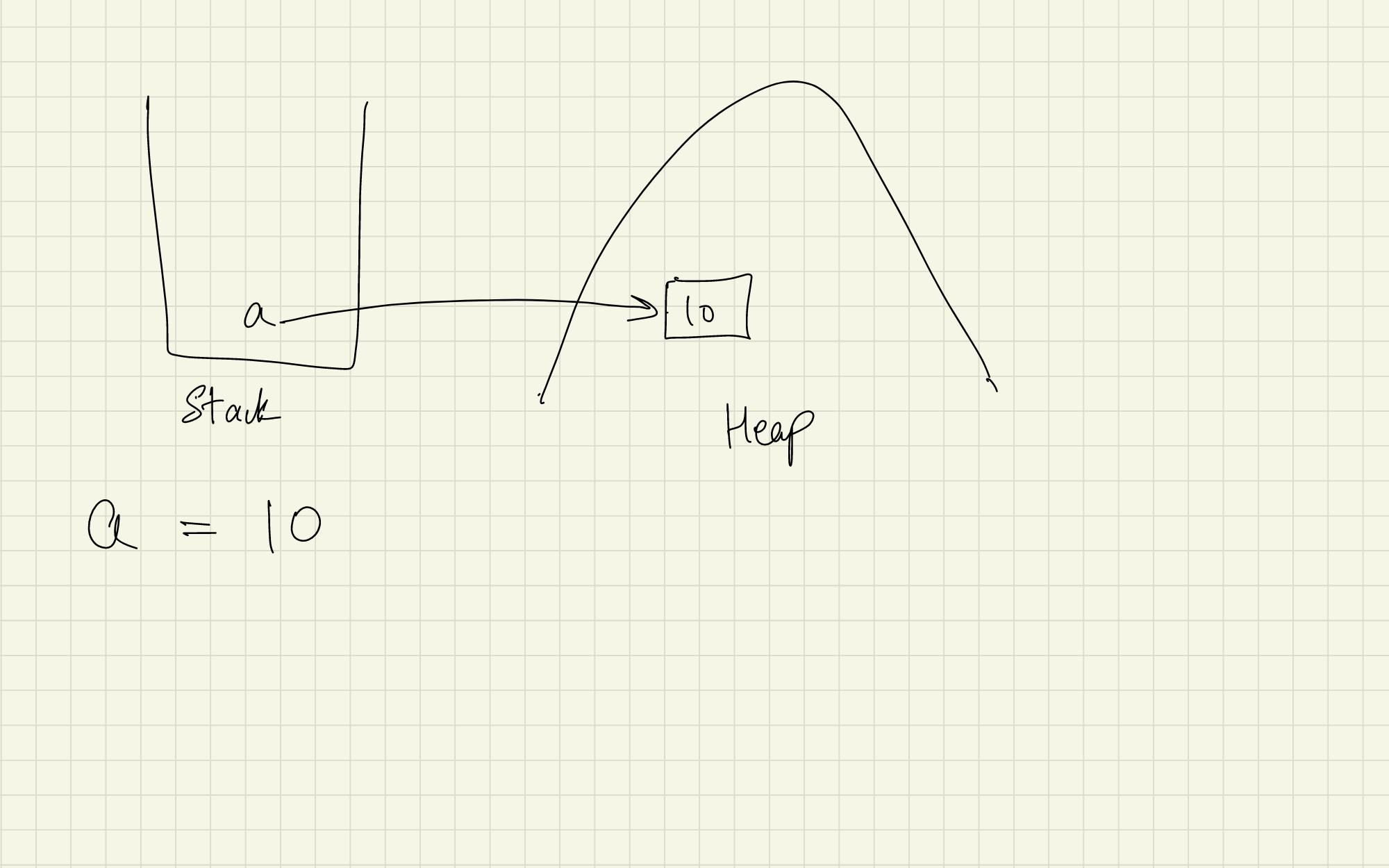
Image Credits: KunalKushwaha
Here in stack, reference variable(a) along the address variable is pointing to the object 10 in heap memory as illustrated in the above image.
More than one reference variables can point to the same object.
Change is visible to all reference variables.
That's all for this article see you in the next one 😊
See you:)
join me on Canva: lavs
Lets catch up!!
- Reach me out at below links:💥
- Github:🙋Github
- LinkedIn: 👸Linkedin
- Youtube: 💬Youtube
- Twitter- 💬Twitter
- Hashnode - 💬Hash Node

