Introduction to Java -Architecture of Java.
In this blog lets check out related to java with architecture and its components.
Introduction:
As we know computer understands only 0's and 1's we need to give instructions in the
same manner.
Programming Languages are used to instruct computers understand the instructions
provided by human.
File Structures:
We write instructions in different file structures.
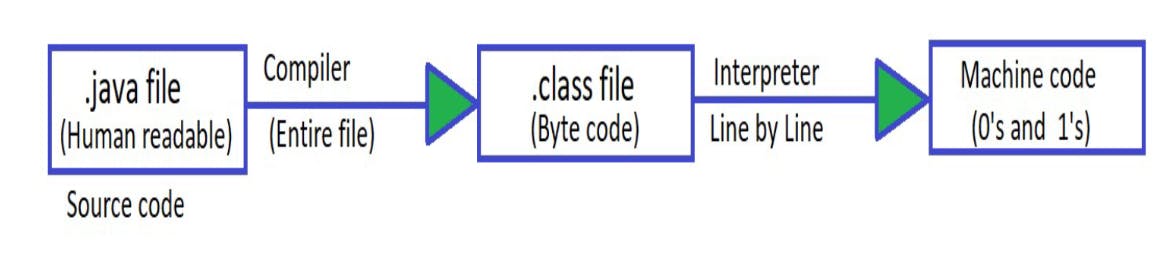
.java file in case of java.
For other like C we use .c file and so on.
In C and C++ we write the code and give the code to compiler.
Here code is compiled by compiler to executable machine code.
But in case of java its converted into byte code and then to machine code so java is
platform independent and can be run from anywhere.
- In case of python interpreter compiles the code.
Interpreter:
Compiles the code line by line.
Compiler:
Take the code and convert it to 0's and 1's. * But in Java we send the code to compiler and the entire file is sent to byte code which is
stored in .class file.
We had byte code because we cant directly run in the system so we use JVM.
JVM means java virtual machine.
The java execution is shown in the below illustrated image.
There will be many confusions regarding the terms so lets have a small discussion on the topics
1. Platform independence:
-Platform independence means the byte code can run on all operating systems.
While compiling C and C++ file we get .exe (executable) file which is platform dependent.
Platform dependent means works only on one platform.
In java it creates byte code where we can use the file in any file or platforms.
In java byte code is created using JVM converts to machine code.
If we have JVM we can run any of files of java but JVM is platform dependent.
Byte code is platform independent.
Architecture of JAVA
JDK-Java Development Kit
JRE - Java Runtime Environment
JVM -Java virtual Machine
JIT-Just in time compiler
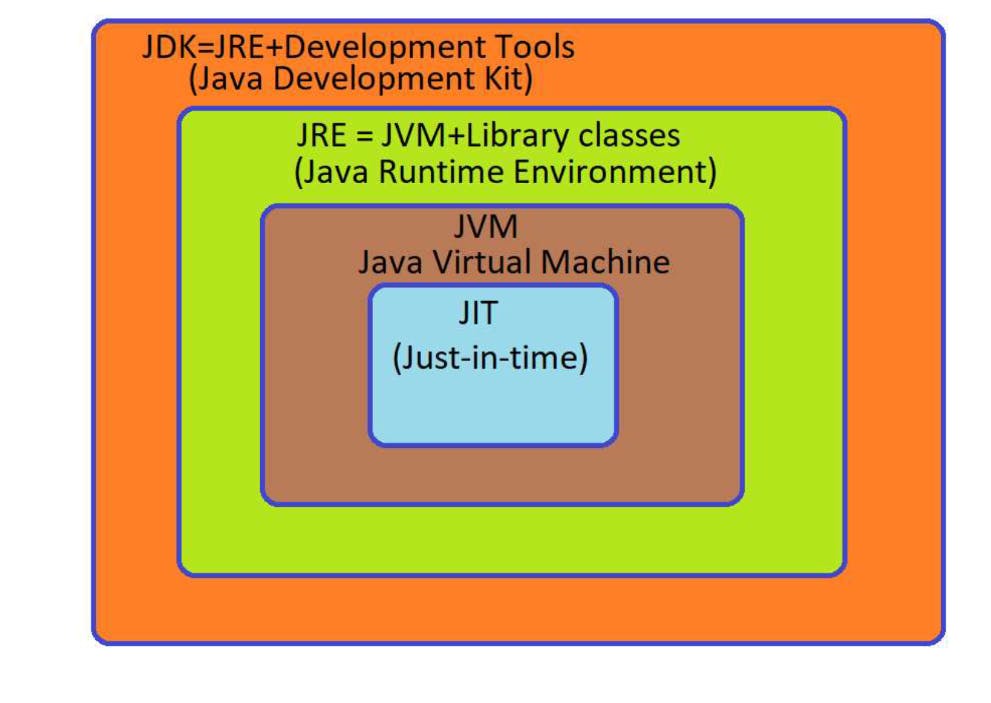
1. JDK
A package or set of files which provides tools to run a program.
Development tools - provides and environment to run a program
JRE - to execute the program
Consists of compiler - javac
Archiver - jar
docs generator - javadoc
6.interpreter / loader
2. JRE -Java Runtime Environment:
installation package that provides an environment to run a program
It consists of
Deployment technologies
User interface tool kits
Integration libraries
Base libraries
3. JVM -Java Virtual Machine:
After the .class file
class loader loads all classes needed to execute the program
JVM sends code to byte code verifier and does code formatting.
Java doesn't have pointers.
Compile time
- .java file compiles to .class file
javac-- java compilation
class Loader
two operations in class loader
Loading
- Reads .class file and creates binary data
An object of this class is created in heap memory
Linking:
Linking contains three steps
Verifies the .class file
allocates memory for class variables and values
replace symbolic references with actual values.
JVM has stack and heap memory allocations.
All values will be assigned to their respective values.
Static means the values are not changed.
JVM execution
Interpreter:
- line by line execution.
- byte file is executed line by line.
- when one method is called many times it will be used again and again.
- byte code is converted to machine code again and again.
So to solve repeating of executions again and again we use JIT.
4. JIT -Just in time
JIT provides machine code so that repetition of interpretation is not required this allows making execution faster
Garbage collection is also used here Garbage collections in short refers to removal of unused variables and values and only uses the declared variables which saves memory
The process of execution can be given as following steps
Java source code - .class file is sent to JDK where it converts to byte code and JVM checks and converts to machine code and JRE runs and checks the packages required to run a program and output is displayed
JRE and JRM are interconnected to each other to perform code compilation and providing required files.
Lets catch up!!
- Reach me out at below links:💥
- Github:🙋Github
- LinkedIn: 👸Linkedin
- Youtube: 💬Youtube
- Twitter- 💬Twitter
- Hashnode - 💬Hash Node

